EVALUATION OF MONEYSENSE ARTICLES RE THE COST OF RETIRING WELL: COUPLES VERSUS SINGLES, DECEMBER, 2014 AND JANUARY, 2015.
These thoughts are purely the blunt, no nonsense personal opinions of the author and are not intended to provide personal or financial advice.
SOURCES OF INFORMATION FOR THIS BLOG POST
MoneySense, December, 2014, “The Cost of Retirement Happiness” by David Aston (couples) /the-cost-of-retirement-happiness/
MoneySense January, 2015, “Single Retirees: The Power of One” by David Aston (singles) /single-retirees-the-power-of-one/
Kudos to MoneySense-they are one of the few sources of information that identify what it truly costs singles to live in comparison to married/coupled persons.
——————————————————————————————————————–
The above articles for couples and singles were presented in two different timeframes by MoneySense. financialfairnessforsingles.ca thought it would be an interesting exercise to combine the figures from both articles and complete an analysis of the figures for the married/coupled retirees versus the singles retirees. (It is important to note that the definition of ‘single’ status by MoneySense is not the same definition used by financialfairnessforsingles.ca and Statistics Canada. The only person who is truly single in the six profiles is Spencer as an ‘ever’ single person (never married, no children), while Reynolds is divorced and McDonald is widowed. This is based on and justified by the Canadian Income Tax forms where the status of the tax filer has to be entered re status of married, single, divorced/separated or widowed and Statistics Canada definitions of marital status).
MoneySense Comments on Retirees Incomes
Couples – According to MoneySense author, a couple should be able to have a middle-class retirement lifestyle spending $42,000 to $72,000 a year including income taxes and assuming there is a paid-for home and no debt. After tax, that will leave about $38,000 to $62,000 a year to spend as couples choose. The minimum of about $38,000 (excluding taxes) should be sufficient to cover the basics, including operating a car and eating healthy. Money Coaches Canada advises keeping annual spending on the basics within the $25,000 to $35,000 range, while trying to ensure there is at least $10,000 for extras, (Dec. /14, article).
Singles – According to MoneySense author, a middle class single retiree should count on spending approximately $30,000 to $50,000 a year including taxes and assuming there is a paid-for home and no debt. This is about 70% of what is required for a couple since it costs about 70% of the couple’s rate for a single to maintain the same lifestyle as a couple.
For $30,000 income, taxes would be about $2,000 to $3,000 for older singles and $3,800 to $5,100 for younger singles below age 65. After taxes and if budget is tight, singles should allow at least $20,000 to $25,000 a year for the basics (including shelter, groceries, transportation and clothing) and at least $5,000 for the extras like entertainment and travel, (Jan. /15, article).
Detailed Financial Information
Couples
Case #1 – It is stated that the Taylors live frugally but comfortably. They have a paid-for three-bedroom home in a nice neighborhood and a ten-year old mid-level car. They eat out occasionally and take regular vacations. They spend just over $25,000 on the basics, which leaves enough left over to spend almost $12,000 on the extras. They both have university educations and held high-paying jobs in the technology industry while raising one child, who now lives independently. Their modest spending habits allowed them to build their savings quickly while working, so they were able to retire in their early 50s and have a large nest egg.
Many advisers tell prospective retirees that they need to replace 70% to 80% of the peak income they had while working, but the Taylors live on less than 20% of the $250,000 they earned while working.
Case #2 – The Statscan couple depicts the average spending by senior couple. (Source: Statistics Canada, Survey of household spending in 2010) plus inflation adjustments using the Consumer Price Index.
Case #3 – The Coopers, both close to 70, have lots of money to do the things they consider important, but don’t live a lavish lifestyle. They spend modestly on the basics, which leaves plenty for the extras that give them the most satisfaction, like travel. Their basic spending, at just under $45,000, isn’t much more than that of the Statscan couple. But by economizing on the basics, they can afford to spend about $36,000 on the extras. They learned frugality early on in life. During their working years, they lived on his public sector professional salary while she had primary responsibility for the household and raising three children. They also benefitted from his pension plan and saved by living well within their means and invested wisely. They have two vehicles (buy them used and keep them well beyond ten years). Now they have far more money than they need to support their accustomed lifestyle.
The Coopers love to spend money for the benefit of their extended family. They have a two-bedroom condo in the city as well as a vacation property. They use their $16,000 travel budget for regular vacations. They even spend some of their budget to cover the cost of extended family joining them on vacation. They also contribute to their grandkids’ RESPs. And while the $6,000 they budget for charitable and personal gifts is not enormous, they have distributed around $500,000 to their kids over the years to give them a good start.
Singles
Case #1 – ‘Ever’ single Spencer is in her early 60s and had to stop working at her physically demanding public sector job over a year ago due to a repetitive stress injury. She hopes to return to work in some role, but even if she is unable to work again she feels she can live comfortably and sustainably on what she now has in savings, as well as government and employer pensions. She has a $38,000 budget and pays $5,000 in income tax. Based on having a paid-for home she will spend about $23,000 on basics which leaves about $10,000 left for the extras. She recently made the choice to move to a small town, mainly for the small town lifestyle, but also for the lower cost of living as well. Money has been set aside to purchase a modest home. (She does state that earlier in life she had some bad spending habits; however, she has learned to make careful, purposeful spending choices).
Case #2 – Reynolds in her early 60s (split up with her partner about ten years ago and no children?) is intent on making the most of retirement and has above-average means to do so. Recently retired after a career in the public sector, she has a budget of $73,000 a year, including about $33,000 for the basics, and a sizeable $25,000 for the extras. She likes to travel and has about $6,000 a year allocated to it. In the early years of her career she was fixated on saving, which helped provide the ample nest egg she has today, including a group RRSP.
Case #3 – McDonald, a widower in his late 60s, has an above average budget of about $81,000, including $41,000 for the basics and $21,000 for the extras. He uses his money to support hobbies, travel and spending on his two grown children and their families. He is trying to find a balance between spending his money and leaving a large legacy. He takes two to three trips a year with his $10,000 budget. His budget also covers some travel for his children and relatives. He spends quite a bit on groceries and restaurants, including paying for meals with extended family. He happily spends less than his ample means would allow.
Qualifying Statements by MoneySense about the two articles
The MoneySense author along with Money Coaches Canada notes that the category ‘shelter’ includes property taxes, utilities, maintenance, house insurance, rent and mortgage payments. Case #3 Statscan figures include a small proportion of costs attributable to a second home. For the ‘vehicle’ category, $2,000 a year has been added for depreciation. The category ‘home and garden’ includes cleaning supplies, furnishings, appliances, garden supplies and services. The category ‘recreation and entertainment’ includes computer equipment and supplies, recreation vehicles, games of chance, and educational costs.
The author also makes the following qualifying statements: “If you are single, you know that retirement planning is tougher for you than it is for couples. You have no one to rely on but yourself, and you can’t share expenses or split income. As a result, you can’t just take the cost of retirement for couples and divide it by two. Situations vary, but a single person will need to spend roughly 70% as much as a couple to enjoy an equivalent lifestyle in retirement…The figure for couples isn’t twice the figure for singles–it is only about 40% higher because spouses are able to share costs for things like housing and cars. The higher per-person income singles need also results in higher taxes”.
Table
The following table combines the financial profiles of the three couples and three singles from the two articles into one table.
Following the table are financialfairnessforsingles.ca comments evaluating the results of the financial profiles.
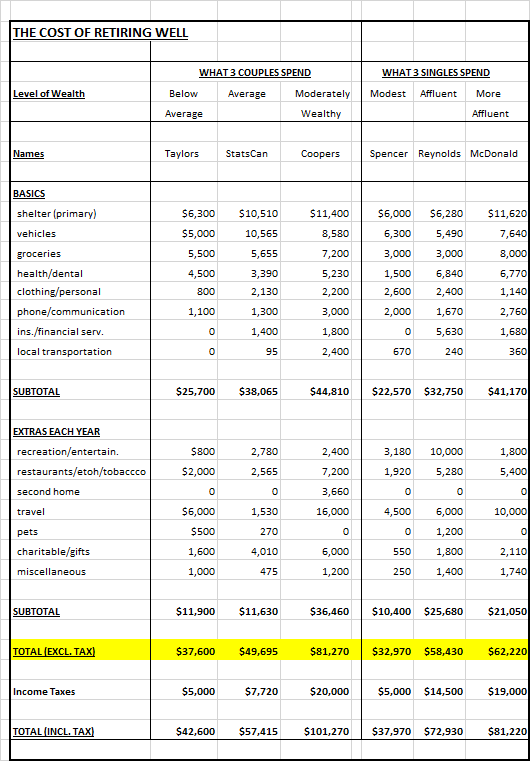
Analysis of the Financial Profiles of Couples Versus Singles
Marital Status
First, it is important to get one fact straight. Couples who divorce/separate and persons who are widowed are not singles. The only person who is truly single in the six profiles is Spencer as an ‘ever’ single person (never married, no children). The profile of the ‘ever’ single person shows that she is likely at the bottom of the financial status list in terms of wealth as she is the one with a modest home in a small town where it is cheaper to live. The separated person likely has a better financial profile because she was able to accumulate wealth as a coupled person for twenty-five or thirty years and was separated later in life (if she had separated earlier in life, she likely would have a financial profile more equal to the ‘ever’ single profile). All of the other profiles show that they have more wealth and homes in nice neighborhoods and even second homes (Coopers).
Benefits
Marital status also determines who is likely to have more benefits. It can be assumed that the couples have the higher financial status simply because they are married or widowed. The married profiles will most likely pay less income tax than the single profiles because couples receive two of everything, have the ability to pension split and can get survivor benefits when widowed, etc. As retirees, the two profiles that lose on benefits are the ‘ever’ single person and the person who is separated.
It is stated that most of the couples have lived so frugally that they now have more money than they need, but at same time have three bedroom houses in nice neighborhood, vacation home, and can retire in their 50s and 60s with a very comfortable lifestyles. This implies, even with frugality, they had plenty of money to spend and save as married/coupled families with children.
The single person is the one that has to move to a smaller town to lower living expenses while others are living in what appears to be substantial housing.
Taxes
On examination of the profiles, it is easy to see that the persons who are paying the most taxes are the ever single person, the separated person and the widowed person. The Taylor couple pays the same taxes as the ‘ever’ single person (Spencer), but they have approximately $5,000 more in income and appear to have much more wealth in terms of assets (must be the pension splitting). It pays to be married. The Statscan couple pays less income tax (almost one half of the amount equal to 13.4%) than the separated Reynolds person (20%), but her income does not come even close to double of the Statscan couple. The Coopers are paying only $20,000 on $100,000 income (20%).
The widowed person (McDonald) with all of his wealth is most likely receiving survivor benefits. Did he pay extra for these benefits and why is he portrayed as being single? If he is now single why should he receive anything more than the ‘ever’ single person and the separated person?
Benefits to Families of Coupled People
The profiles of the coupled persons and the previously coupled person (widower McDonald) blatantly state that they have more money than they can spend and have given generous monetary gifts, paid for the meals of their kids, grandchildren and extended family members, etc.
Married/coupled people or previously coupled people are often able to give exorbitant gifts, inheritances, etc. to family and extended family. Does this not create a sense of entitlement for family, children and grandchildren who begin to expect this all the time? How does this extravagance teach frugality?
Emergency Monies
Where in any of these profiles has money been set aside for emergencies? The person most likely to be unable to pay for financial emergencies due to illness, financial issues, etc. is the ever single person with the least accumulation of wealth.
Education, Education, Education!!!
It is beyond comprehension on how governments, families, society and think tanks lack knowledge and are financially illiterate on the true facts of how ‘ever’ singles and divorced/separated retirees are financially robbed to subsidize married/coupled retirees by paying more taxes while getting less benefits like pension splitting and widower benefits in this country.
Singles require 70% of the income/wealth of Couples
How many ways can this fact be stated and how many different sources of information does the government and society need to make changes on how singles are financially discriminated against in this country?? Do Members of Parliament ever think to include singles when making important decisions like pension splitting and benefits that benefit only the married/coupled and families of this country? Government, businesses, society and media only ever talk about middle class families. Singles meanwhile have been financially discriminated against by their government and society.
How expensive is it to raise a child?
So how expensive is it to raise one child, two children, and three children and still come out on top in terms of wealth in the personal profiles? Governments, society and families, think tanks continue to talk about how expensive it is to raise a child, and yet many families are able to leave large legacies/inheritances to their children. Unfortunately, based on the facts this seems to be based on the half-truths and lies of governments, society, families and think tanks.
Profiling
Singles are often profiled as having excessive spending habits/lifestyles while married/coupled persons are usually profiled as being frugal. Married/coupled persons in their retired state are still profiled as being frugal even though they can give extravagant gifts (in one case around $500,000) to their children and grandchildren and spend more money on items like vacations.
Happy, happy, happy!!!!!
In both articles the profiles and the author comments seem to imply that everyone is happy, happy, and happy with their financial status. ‘Ever’ singles and divorced/separated retirees are blatantly told they should be happy with what they have even though they have been discriminated against financially.
‘Ever’ single persons and divorced/separated persons not so lucky to have achieved equivalent wealth (70%) of married/coupled persons as shown in above examples wish to state they are not happy with being financially discriminated against on every level of government and society. They are not asking for more than married/coupled people. They are asking for financial fairness.
FINAL STATEMENT
Governments, businesses, society, families, think tanks all maintain that the middle class is being affected most by poverty. The real truth is that ‘ever’ singles, singles with kids, persons divorced/separated early in marriage/coupling, and families with low incomes are being affected most by poverty. Singles (‘ever’ and divorced/separated) in this country are not happy with always being excluded from financial formulas and conversations. They are human and in their humanity are equal to married/coupled people, and it is time that they are treated with the same financial fairness, dignity and respect as married/coupled people.
This blog is of a general nature about financial discrimination of individuals/singles. It is not intended to provide personal or financial advice.





